PyG 2.0 Released
PyG (PyTorch Geometric) has been moved from the personal account rusty1s to its own organization account pyg-team to emphasize the ongoing collaboration between TU Dortmund University, Stanford University and many great external contributors.
With this, we are releasing PyG 2.0, a new major release that brings sophisticated heterogeneous graph support, GraphGym and many other exciting features to PyG.
Heterogeneous Graph Support
We finally provide full heterogeneous graph support in PyG 2.0. See here for the accompanying tutorial.
Highlights
- Heterogeneous Graph Storage: Heterogeneous graphs can now be stored in their own dedicated
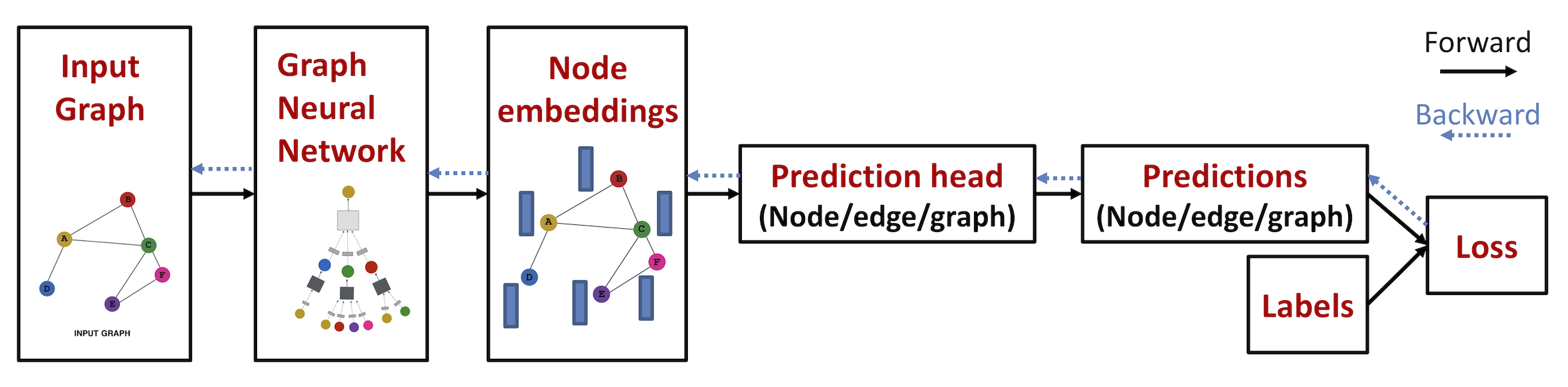
data.HeteroDataclass (thanks to @yaoyaowd):from torch_geometric.data import HeteroData data = HeteroData() # Create two node types "paper" and "author" holding a single feature matrix: data['paper'].x = torch.randn(num_papers, num_paper_features) data['author'].x = torch.randn(num_authors, num_authors_features) # Create an edge type ("paper", "written_by", "author") holding its graph connectivity: data['paper', 'written_by', 'author'].edge_index = ... # [2, num_edges]data.HeteroDatabehaves similar to a regular homgeneousdata.Dataobject:print(data['paper'].num_nodes) print(data['paper', 'written_by', 'author'].num_edges) data = data.to('cuda') - Heterogeneous Mini-Batch Loading: Heterogeneous graphs can be converted to mini-batches for many small and single giant graphs via the
loader.DataLoaderandloader.NeighborLoaderloaders, respectively. These loaders can now handle both homogeneous and heterogeneous graphs:from torch_geometric.loader import DataLoader loader = DataLoader(heterogeneous_graph_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True) from torch_geometric.loader import NeighborLoader loader = NeighborLoader(heterogeneous_graph, num_neighbors=[30, 30], batch_size=128, input_nodes=('paper', data['paper'].train_mask), shuffle=True) - Heterogeneous Graph Neural Networks: Heterogeneous GNNs can now easily be created from homogeneous ones via
nn.to_heteroandnn.to_hetero_with_bases. These processes take an existing GNN model and duplicate their message functions to account for different node and edge types:from torch_geometric.nn import SAGEConv, to_hetero class GNN(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(hidden_channels, out_channels): super().__init__() self.conv1 = SAGEConv((-1, -1), hidden_channels) self.conv2 = SAGEConv((-1, -1), out_channels) def forward(self, x, edge_index): x = self.conv1(x, edge_index).relu() x = self.conv2(x, edge_index) return x model = GNN(hidden_channels=64, out_channels=dataset.num_classes) model = to_hetero(model, data.metadata(), aggr='sum')
Additional Features
- A heterogeneous graph tutorial describing all newly released features (thanks to @mrjel)
- A variety of heterogeneous GNN examples
- Support for lazy initialization of GNN operators by passing
-1to thein_channelsargument (implemented viann.dense.Linear). This allows to avoid calculating and keeping track of input tensor sizes, simplyfing the creation of heterogeneous graph models with varying feature dimensionalities across different node and edge types. Lazy initialization is supported for all existing PyG operators (thanks to @yaoyaowd):from torch_geometric.nn import GATConv conv = GATConv(-1, 64) # We can initialize the model’s parameters by calling it once: conv(x, edge_index) nn.conv.HeteroConv: A generic wrapper for computing graph convolution on heterogeneous graphs (thanks to @RexYing)nn.conv.HGTConv: The heterogeneous graph transformer operator from the “Heterogeneous Graph Transformer” paperloader.HGTLoader: The heterogeneous graph sampler from the “Heterogeneous Graph Transformer” paper for learning on large-scale heterogeneous graphs (thanks to @chantat)- Support for heterogeneous graph transformations in
transforms.AddSelfLoops,transforms.ToSparseTensor,transforms.NormalizeFeaturesandtransforms.ToUndirected - New heterogeneous graph datasets:
datasets.OGB_MAG,datasets.IMDB,datasets.DBLPanddatasets.LastFM - Support for converting heterogeneous graphs to “typed” homogeneous ones via
data.HeteroData.to_homogeneous(thanks to @yzhao062) - A tutorial on creating a
data.HeteroDataobject from raw*.csvfiles (thanks to @yaoyaowd and @mrjel) - An example to scale heterogeneous graph models via PyTorch Lightning
Managing Experiments with GraphGym
GraphGym is now officially supported in PyG 2.0 via torch_geometric.graphgym.
See here for the accompanying tutorial.
Overall, GraphGym is a platform for designing and evaluating Graph Neural Networks from configuration files via a highly modularized pipeline (thanks to @JiaxuanYou):
- GraphGym is the perfect place to start learning about standardized GNN implementation and evaluation
- GraphGym provides a simple interface to try out thousands of GNN architectures in parallel to find the best design for your specific task
- GraphGym lets you easily do hyper-parameter search and visualize what design choices are better
Breaking Changes
- The
datasets.AMinerdataset now returns adata.HeteroDataobject. See here for our updatedMetaPath2Vecexample onAMiner. transforms.AddTrainValTestMaskhas been replaced in favour oftransforms.RandomNodeSplit- Since the storage layout of
data.Datasignificantly changed in order to support heterogenous graphs, already processed datasets need to be re-processed by deleting theroot/processedfolder. data.Data.__cat_dim__anddata.Data.__inc__now expect additional input arguments:def __cat_dim__(self, key, value, *args, **kwargs): pass def __inc__(self, key, value, *args, **kwargs): passIn case you modified
__cat_dim__or__inc__functionality in a customizeddata.Dataobject, please ensure to apply the above changes.
Deprecations
nn.conv.PointConvis deprecated in favour ofnn.conv.PointNetConv(thanks to @lelouedec and @QuanticDisaster)utils.train_test_split_edgesis deprecated in favour of the newtransforms.RandomLinkSplittransform- All data loaders were moved from
torch_geometric.datatotorch_geometric.loader, e.g.:from torch_geometric.loader import DataLoader loader.NeighborSampleris deprecated in favour ofloader.NeighborLoaderin order to simplify the application of neighbor sampling and to support both neighbor sampling in homogeneous and heterogeneous graphsData.contains_isolated_nodesandData.contains_self_loopsare deprecated in favour ofData.has_isolated_nodesandData.has_self_loops, respectively
Additional Features
torch-scatterandtorch-sparsenow support half-precision computation viatorch.half, bringing half-precision support to PyG- Added a GNN cheatsheet to the documentation, which lets you more easily choose a GNN operator for your specific need
- Added the
transforms.RandomLinkSplittransform to easily perform a random edge-level random split (thanks to @RexXing) - Added the
torch_geometric.profilepackage which provides a variety of utility functions for benchmarking runtimes and memory consumptions of GNN models (thanks to @yzhao062) nn.conv.MessagePassingnow supports hooks forpropagate,message,aggregateandupdatefunctions, e.g. viann.conv.MessagePassing.register_propagate_forward_hook- Added the
nn.conv.GeneralConvoperator that can handle most GNN use-cases (e.g., w/ or w/o edge features, …) and has enough design options to be tuned (e.g., attention, skip-connections, …) (thanks to @JiaxuanYou) - Added the
nn.models.RECT_Lmodel for learning with completely-imbalanced labels (thanks to @Fizyhsp) - Added the Pathfinder Discovery Network Convolutional operator
nn.conv.PDNConv(thanks to @benedekrozemberczki) - Added basic GNN model support as part of the
nn.modelspackage, e.g.,nn.model.GCN,nn.models.GraphSAGE,nn.models.GATandnn.models.GIN. Pre-defined models support customizing hidden feature dimensionality, number of layers, activation, normalization and jumping knowledge (thanks to @PabloAMC) - Added the
datasets.MD17datasets (thanks to @M-R-Schaefer) - Added a link-prediction example of
nn.conv.RGCNConv(thanks to @moritzblum) - Added an example of
nn.pool.MemPooling(thanks to @wsad1) - Added a
return_attention_weightsargument fornn.conv.TransformerConv(thanks to @wsad1) - Batch support for
utils.homophily(thanks to @wsad1) - Added a
batch_sizeargument toutils.to_dense_batch(thanks to @jimmiebtlr)
Minor Changes
- Heavily improved loading times of
import torch_geometric nn.Sequentialis now fully jittablenn.conv.LEConvis now fully jittable (thanks to @lucagrementieri)nn.conv.GENConvcan now make use of"add","mean"or"max"aggregations (thanks to @riskiem)- Attributes of type
torch.nn.utils.rnn.PackedSequenceare now correctly handled bydata.Dataanddata.HeteroData(thanks to @WuliangHuang) - Added support for
data.record_stream()in order to allow for data prefetching (thanks to @FarzanT) - Added a
max_num_neighborsattribute tonn.models.SchNetandnn.models.DimeNet(thanks to @nec4) nn.conv.MessagePassingis now jittable in casemessage,aggregateandupdatereturn multiple arguments (thanks to @PhilippThoelke)utils.from_networkxnow supports grouping of node-level and edge-level features (thanks to @PabloAMC)- Transforms now inherit from
transforms.BaseTransformto ease type checking (thanks to @CCInc) - Added support for the deletion of data attributes via
del data[key](thanks to @Linux-cpp-lisp)
Bugfixes
- The
transforms.LinearTransformationtransform now correctly transposes the input matrix before applying the transformation (thanks to @beneisner) - Fixed a bug in
benchmark/kernelthat prevented the application ofDiffPoolon theIMDB-BINARYdataset (thanks to @dongZheX) - Feature dimensionalities of
datasets.WikipediaNetworkdo now match which the official reported ones in casegeom_gcn_preprocess=True(thanks to @ZhuYun97 and @GitEventhandler) - Fixed a bug in the
datasets.DynamicFAUSTdataset in whichdata.num_nodeswas undefined (thanks to @koustav123) - Fixed a bug in which
nn.models.GNNExplainercould not handle GNN operators that add self-loops to the graph in case self-loops were already present (thanks to @tw200464tw and @NithyaBhasker) nn.norm.LayerNormmay no longer produce NaN gradients (thanks to @fbragman)- Fixed a bug in which it was not possible to customize
networkxdrawing arguments innn.models.GNNExplainer.visualize_subgraph()(thanks to @jvansan) transforms.RemoveIsolatedNodesnow correctly removes isolated nodes in casedata.num_nodesis explicitely set (thanks to @blakechi)